Active Checks
Need Help Configuring Nagios?
Our tech support team is happy to help you with any questions you might have. Contact us on our online support forum at https://support.nagios.com/forum/
Nagios XI Makes Monitoring Easier:
Nagios XI is the easy-to-use, enterprise version of Nagios that features:
- Web-Based Configuration provides advanced configuration features
- Monitoring Wizards make it easy to monitor new devices, applications, and services
- Customizable Dashboards allow for per-user customization
- Integrated Performance Graphs provide trending and capacity planning information
- Advanced Reports provide data insight and exporting capabilities
- Data Visualizations enable powerful analysis of patterns and problems
- Nagios Core Import functionality makes it easy to migrate from Nagios Core
- ... and many other features
Download a free 30-day trial to give Nagios XI a spin.
Inquire today and let our Quickstart team help you get started with Nagios XI
 Up To: Contents
Up To: Contents
 See Also: Passive Checks, Plugins, Service Checks, Host Checks
See Also: Passive Checks, Plugins, Service Checks, Host Checks
Introduction
Nagios Core is capable of monitoring hosts and services in two ways: actively and passively. Passive checks are described elsewhere, so we'll focus on active checks here. Active checks are the most common method for monitoring hosts and services. The main features of actives checks as as follows:
- Active checks are initiated by the Nagios Core process
- Active checks are run on a regularly scheduled basis
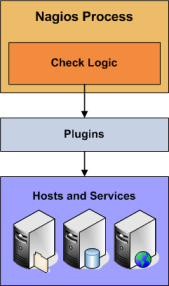
How Are Active Checks Performed?
Active checks are initiated by the check logic in the Nagios Core daemon. When Nagios Core needs to check the status of a host or service it will execute a plugin and pass it information about what needs to be checked. The plugin will then check the operational state of the host or service and report the results back to the Nagios Core daemon. Nagios Core will process the results of the host or service check and take appropriate action as necessary (e.g. send notifications, run event handlers, etc).
More information on how plugins work can be found here.
When Are Active Checks Executed?
Active check are executed:
- At regular intervals, as defined by the check_interval and retry_interval options in your host and service definitions
- On-demand as needed
Regularly scheduled checks occur at intervals equaling either the check_interval or the retry_interval in your host or service definitions, depending on what type of state the host or service is in. If a host or service is in a HARD state, it will be actively checked at intervals equal to the check_interval option. If it is in a SOFT state, it will be checked at intervals equal to the retry_interval option.
On-demand checks are performed whenever Nagios Core sees a need to obtain the latest status information about a particular host or service. For example, when Nagios Core is determining the reachability of a host, it will often perform on-demand checks of parent and child hosts to accurately determine the status of a particular network segment. On-demand checks also occur in the predictive dependency check logic in order to ensure Nagios Core has the most accurate status information.